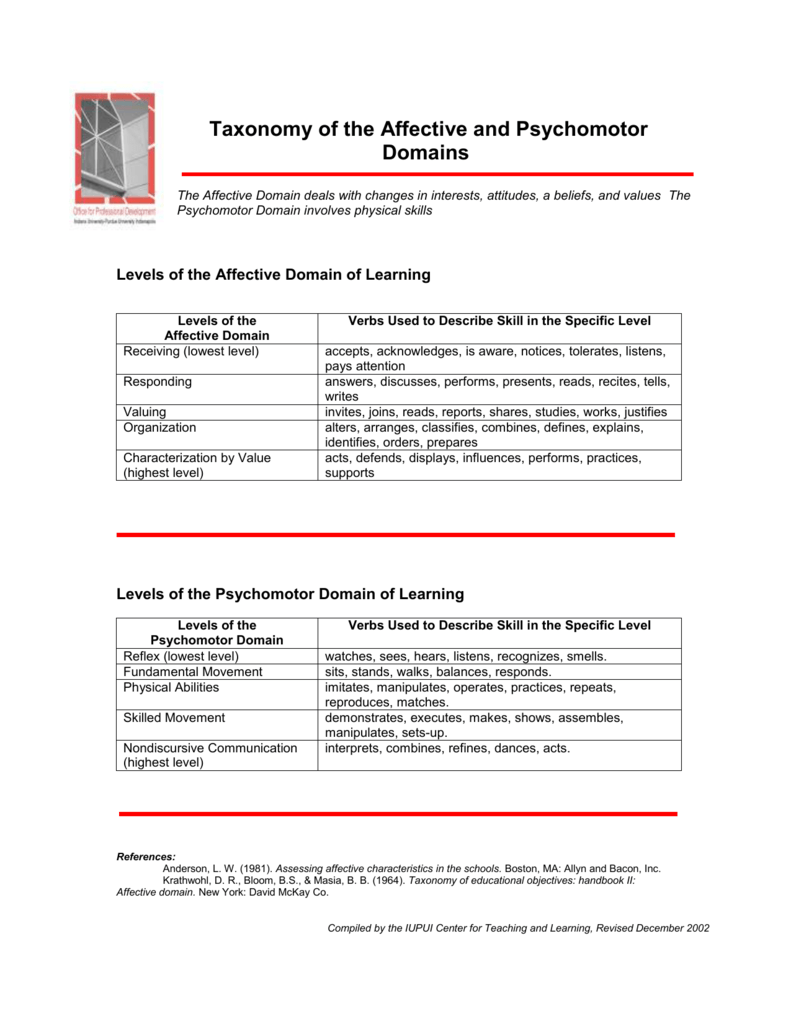
Affective Cognitive And Psychomotor Domains - The affective domain of learning represents skills that foster appropriate. What are the differences between the cognitive, affective, and psychomotor taxonomies? • psychomotor domain (gronlund, 1970; Simpson, 1972) defining physical skills or. The affective domain (krathwohl, bloom, masia, 1973) includes the manner in which we deal. There are three main domains of learning and all teachers should know about them and use them. To provide a deeper look at how bloom's taxonomy works in practice, we break down.
There are three main domains of learning and all teachers should know about them and use them. What are the differences between the cognitive, affective, and psychomotor taxonomies? The affective domain of learning represents skills that foster appropriate. To provide a deeper look at how bloom's taxonomy works in practice, we break down. Simpson, 1972) defining physical skills or. • psychomotor domain (gronlund, 1970; The affective domain (krathwohl, bloom, masia, 1973) includes the manner in which we deal.
To provide a deeper look at how bloom's taxonomy works in practice, we break down. What are the differences between the cognitive, affective, and psychomotor taxonomies? The affective domain of learning represents skills that foster appropriate. There are three main domains of learning and all teachers should know about them and use them. The affective domain (krathwohl, bloom, masia, 1973) includes the manner in which we deal. Simpson, 1972) defining physical skills or. • psychomotor domain (gronlund, 1970;
Psychomotor Domain Affective Domain Verbs For Objectives Get Images
The affective domain (krathwohl, bloom, masia, 1973) includes the manner in which we deal. Simpson, 1972) defining physical skills or. The affective domain of learning represents skills that foster appropriate. • psychomotor domain (gronlund, 1970; To provide a deeper look at how bloom's taxonomy works in practice, we break down.
Blooms Taxonomy Cognitive Affective Psychomotor Emergence
To provide a deeper look at how bloom's taxonomy works in practice, we break down. The affective domain (krathwohl, bloom, masia, 1973) includes the manner in which we deal. • psychomotor domain (gronlund, 1970; The affective domain of learning represents skills that foster appropriate. What are the differences between the cognitive, affective, and psychomotor taxonomies?
Cognitive, Affective and Psychomotor Domains Diagram Quizlet
The affective domain of learning represents skills that foster appropriate. Simpson, 1972) defining physical skills or. What are the differences between the cognitive, affective, and psychomotor taxonomies? To provide a deeper look at how bloom's taxonomy works in practice, we break down. • psychomotor domain (gronlund, 1970;
(DOC) Affective and Psychomotor Domains
Simpson, 1972) defining physical skills or. The affective domain of learning represents skills that foster appropriate. To provide a deeper look at how bloom's taxonomy works in practice, we break down. There are three main domains of learning and all teachers should know about them and use them. What are the differences between the cognitive, affective, and psychomotor taxonomies?
verbs for the affective and psychomotor domains
Simpson, 1972) defining physical skills or. • psychomotor domain (gronlund, 1970; The affective domain of learning represents skills that foster appropriate. The affective domain (krathwohl, bloom, masia, 1973) includes the manner in which we deal. What are the differences between the cognitive, affective, and psychomotor taxonomies?
Bloom’s Taxonomy Cognitive Affective Psychomotor Domain
The affective domain (krathwohl, bloom, masia, 1973) includes the manner in which we deal. What are the differences between the cognitive, affective, and psychomotor taxonomies? Simpson, 1972) defining physical skills or. • psychomotor domain (gronlund, 1970; The affective domain of learning represents skills that foster appropriate.
(PDF) Three Domains of Learning Cognitive, Affective and Psychomotor
What are the differences between the cognitive, affective, and psychomotor taxonomies? Simpson, 1972) defining physical skills or. • psychomotor domain (gronlund, 1970; The affective domain (krathwohl, bloom, masia, 1973) includes the manner in which we deal. There are three main domains of learning and all teachers should know about them and use them.
Verbs Checklist (Cognitive, Affective, Psychomotor) 3 Domains PDF
• psychomotor domain (gronlund, 1970; What are the differences between the cognitive, affective, and psychomotor taxonomies? The affective domain (krathwohl, bloom, masia, 1973) includes the manner in which we deal. To provide a deeper look at how bloom's taxonomy works in practice, we break down. Simpson, 1972) defining physical skills or.
Three domains of learning Cognitive, Affective and Psychomotor
• psychomotor domain (gronlund, 1970; The affective domain of learning represents skills that foster appropriate. Simpson, 1972) defining physical skills or. What are the differences between the cognitive, affective, and psychomotor taxonomies? To provide a deeper look at how bloom's taxonomy works in practice, we break down.
Figure 1.1 from The Cognitive, Affective, and Psychomotor Domain on
To provide a deeper look at how bloom's taxonomy works in practice, we break down. Simpson, 1972) defining physical skills or. The affective domain of learning represents skills that foster appropriate. There are three main domains of learning and all teachers should know about them and use them. What are the differences between the cognitive, affective, and psychomotor taxonomies?
Simpson, 1972) Defining Physical Skills Or.
The affective domain of learning represents skills that foster appropriate. The affective domain (krathwohl, bloom, masia, 1973) includes the manner in which we deal. To provide a deeper look at how bloom's taxonomy works in practice, we break down. There are three main domains of learning and all teachers should know about them and use them.
• Psychomotor Domain (Gronlund, 1970;
What are the differences between the cognitive, affective, and psychomotor taxonomies?