Phosphodiester Bond Formation - The phosphodiester bond is a covalent linkage between the phosphate of one nucleotide and. A phospodiester bond is a covalent bond in which a phosphate group joins adjacent. In dna and rna, the phosphodiester bond is the linkage between the 3' carbon atom of one. The phosphate group of the 5 ′ carbon of one nucleotide and the 3 ′ carbon of another.
The phosphodiester bond is a covalent linkage between the phosphate of one nucleotide and. The phosphate group of the 5 ′ carbon of one nucleotide and the 3 ′ carbon of another. A phospodiester bond is a covalent bond in which a phosphate group joins adjacent. In dna and rna, the phosphodiester bond is the linkage between the 3' carbon atom of one.
In dna and rna, the phosphodiester bond is the linkage between the 3' carbon atom of one. A phospodiester bond is a covalent bond in which a phosphate group joins adjacent. The phosphate group of the 5 ′ carbon of one nucleotide and the 3 ′ carbon of another. The phosphodiester bond is a covalent linkage between the phosphate of one nucleotide and.
9 Formation of phosphodiester bond between deoxyribose sugars
In dna and rna, the phosphodiester bond is the linkage between the 3' carbon atom of one. A phospodiester bond is a covalent bond in which a phosphate group joins adjacent. The phosphodiester bond is a covalent linkage between the phosphate of one nucleotide and. The phosphate group of the 5 ′ carbon of one nucleotide and the 3 ′.
ROSALIND Glossary Phosphodiester bond
A phospodiester bond is a covalent bond in which a phosphate group joins adjacent. The phosphate group of the 5 ′ carbon of one nucleotide and the 3 ′ carbon of another. The phosphodiester bond is a covalent linkage between the phosphate of one nucleotide and. In dna and rna, the phosphodiester bond is the linkage between the 3' carbon.
12.nucleotidesformationofphosphodiesterbonds.004 The Theoretical
The phosphodiester bond is a covalent linkage between the phosphate of one nucleotide and. The phosphate group of the 5 ′ carbon of one nucleotide and the 3 ′ carbon of another. In dna and rna, the phosphodiester bond is the linkage between the 3' carbon atom of one. A phospodiester bond is a covalent bond in which a phosphate.
Process of formation of Phosphodiester bond Stock Vector Adobe Stock
The phosphodiester bond is a covalent linkage between the phosphate of one nucleotide and. A phospodiester bond is a covalent bond in which a phosphate group joins adjacent. In dna and rna, the phosphodiester bond is the linkage between the 3' carbon atom of one. The phosphate group of the 5 ′ carbon of one nucleotide and the 3 ′.
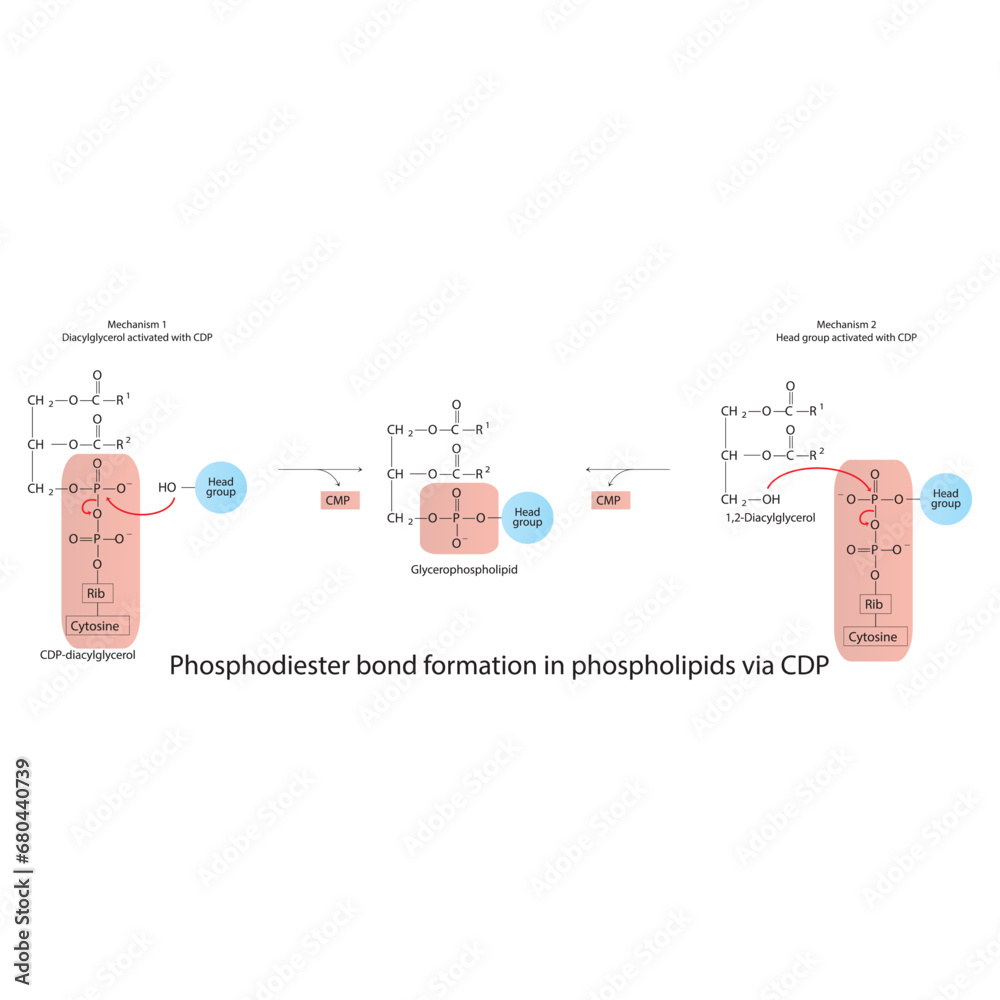
Schematic molcular diagram of phosphodiester bond formation in
The phosphodiester bond is a covalent linkage between the phosphate of one nucleotide and. In dna and rna, the phosphodiester bond is the linkage between the 3' carbon atom of one. The phosphate group of the 5 ′ carbon of one nucleotide and the 3 ′ carbon of another. A phospodiester bond is a covalent bond in which a phosphate.
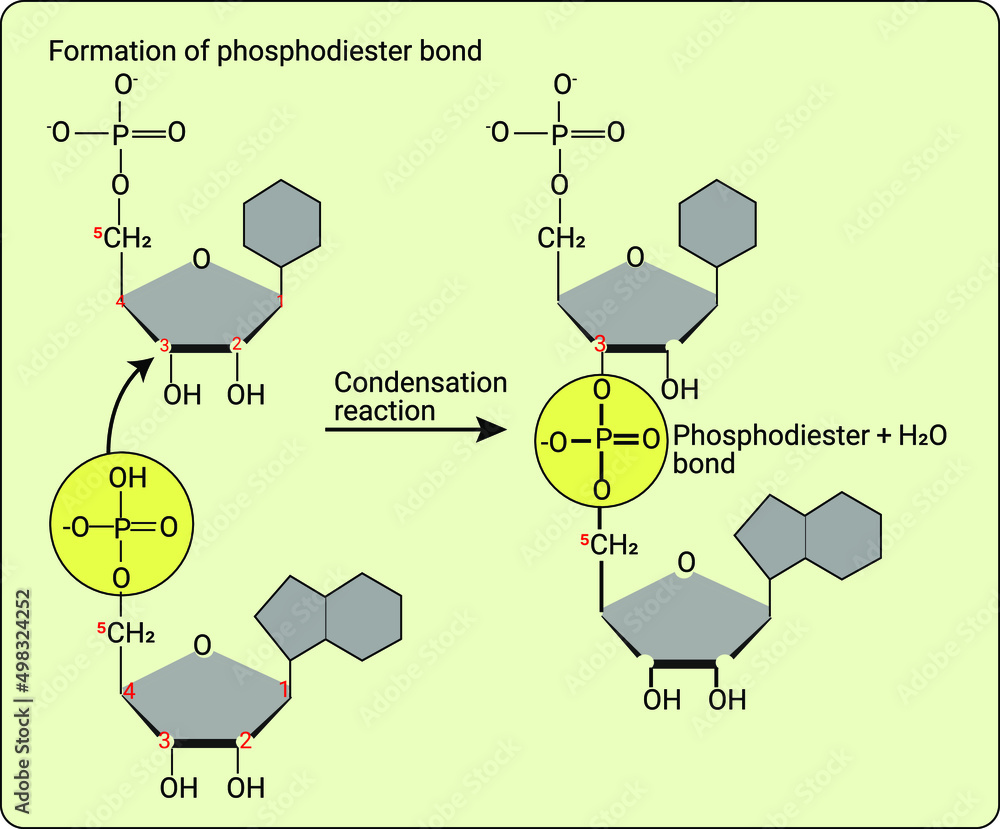
Formation of the phosphodiester bond through the condensation reaction
A phospodiester bond is a covalent bond in which a phosphate group joins adjacent. The phosphodiester bond is a covalent linkage between the phosphate of one nucleotide and. In dna and rna, the phosphodiester bond is the linkage between the 3' carbon atom of one. The phosphate group of the 5 ′ carbon of one nucleotide and the 3 ′.
Schematic molcular diagram of phosphodiester bond formation in
In dna and rna, the phosphodiester bond is the linkage between the 3' carbon atom of one. The phosphodiester bond is a covalent linkage between the phosphate of one nucleotide and. A phospodiester bond is a covalent bond in which a phosphate group joins adjacent. The phosphate group of the 5 ′ carbon of one nucleotide and the 3 ′.
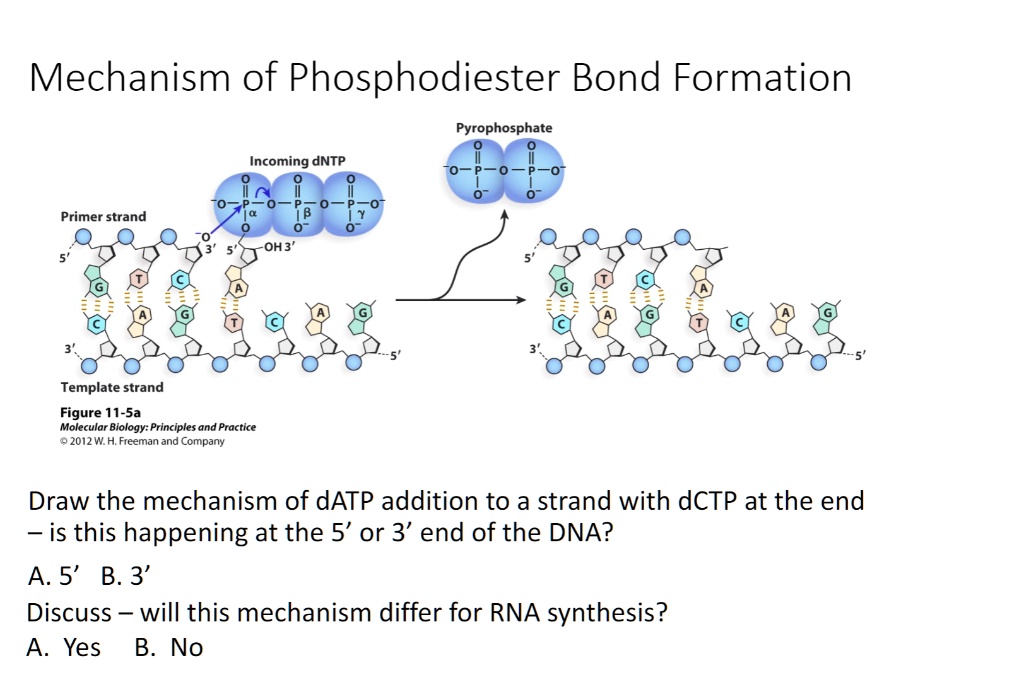
mechanism of phosphodiester bond formation pyrophosphate dntp
A phospodiester bond is a covalent bond in which a phosphate group joins adjacent. The phosphate group of the 5 ′ carbon of one nucleotide and the 3 ′ carbon of another. The phosphodiester bond is a covalent linkage between the phosphate of one nucleotide and. In dna and rna, the phosphodiester bond is the linkage between the 3' carbon.
Formation of the phosphodiester bond through the condensation reaction
The phosphate group of the 5 ′ carbon of one nucleotide and the 3 ′ carbon of another. A phospodiester bond is a covalent bond in which a phosphate group joins adjacent. The phosphodiester bond is a covalent linkage between the phosphate of one nucleotide and. In dna and rna, the phosphodiester bond is the linkage between the 3' carbon.
Phosphodiester Bond in DNA & RNA Linkage, Formation & Function
A phospodiester bond is a covalent bond in which a phosphate group joins adjacent. The phosphate group of the 5 ′ carbon of one nucleotide and the 3 ′ carbon of another. The phosphodiester bond is a covalent linkage between the phosphate of one nucleotide and. In dna and rna, the phosphodiester bond is the linkage between the 3' carbon.
In Dna And Rna, The Phosphodiester Bond Is The Linkage Between The 3' Carbon Atom Of One.
A phospodiester bond is a covalent bond in which a phosphate group joins adjacent. The phosphodiester bond is a covalent linkage between the phosphate of one nucleotide and. The phosphate group of the 5 ′ carbon of one nucleotide and the 3 ′ carbon of another.